Solar Keratoses or Actinic Keratoses
Actinic Keratoses (AKs) I(also known as solar keratoses)are one of the most common “sun spots” seen in Australia.
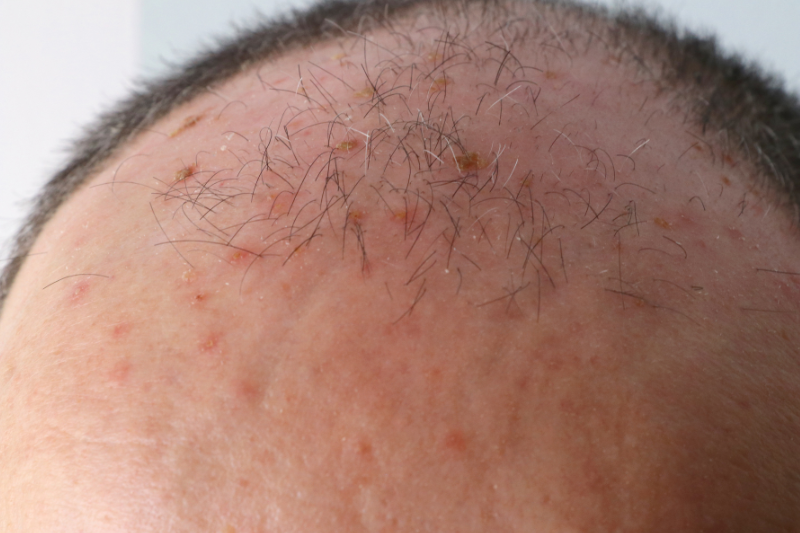
- They appear as red, scaling areas of the skin on parts of the body that are frequently exposed to sunlight. Most notably they occur on the face, ears, neck, arms and hands. They vary in size from 2mm to 20 mm in diameter and frequently “join up” to involve large areas of skin.
- They are not painful or itchy, but may sting when exposed to sunlight or if they are rubbed or scratched.
- They often become more prominent in the summer.
AKs are not skin cancers, but over time they may develop into Squamous Cell Carcinomas (SCC). They develop in response to long years of sun exposure and become more common with increasing age. AKs indicate severely sun damaged skin and are a warning sign that the skin has become prone to all forms of cancer.
The choice of treatment depends upon whether localised lesions or whole areas/regions are to be treated.
Localised treatment options include:
- Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen)
- Shave excision/curettage
- CO2 Laser- used for large lesions
Field treatments for larger areas include:
- Efudix
- Aldara
- Combinations of the above may be employed in certain situations

