Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
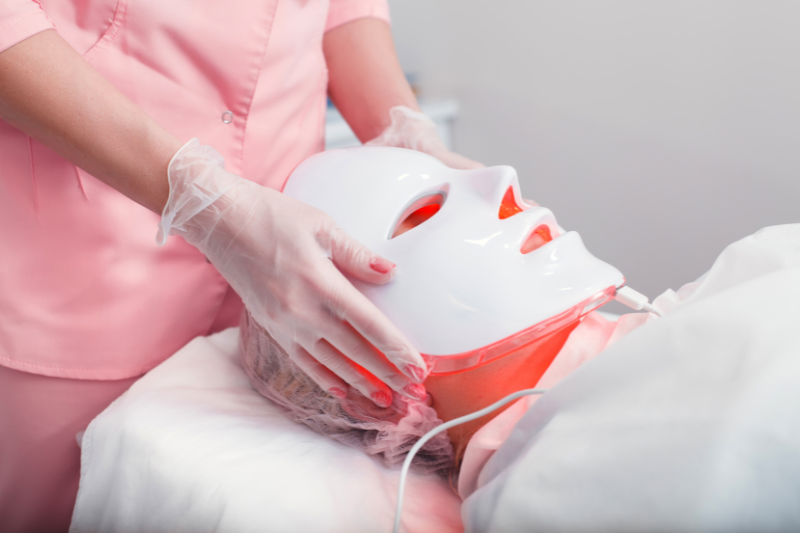
What is PDT?
Is PDT a new Treatment?
Is PDT safe?
What conditions are treated with PDT?
- Surface based skin cancer
- Superficial BCC
- SCC in situ (Bowens Disease)
- Actinic Keratoses (AK)- individually or multiply over an area of abnormal skin
- Actinic cheilitis (precancerous change on lower lip)
- Sun damaged skin for purposes of rejuvenation
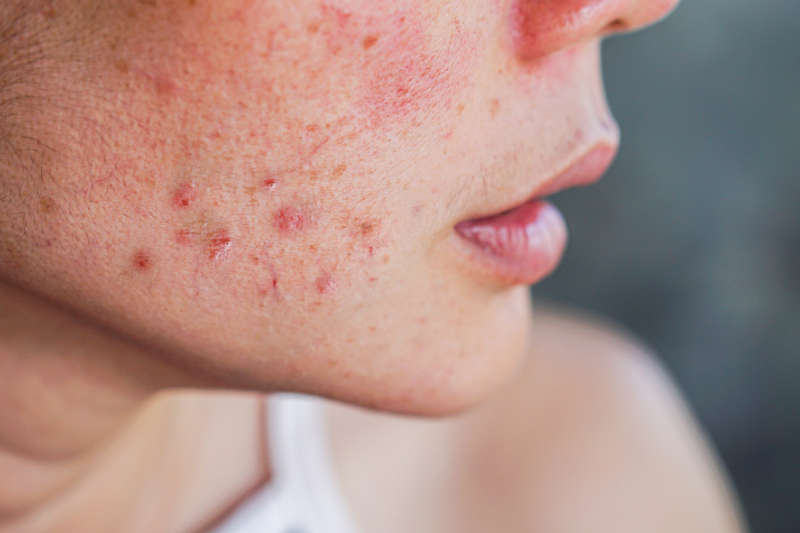
- Miscellaneous- acne, warts and rosacea
Initially the doctor will mark out the area to be treated, and gently curettes (scrapes) the surface of the lesion(s) to be treated.
ALA cream is then applied by a Nurse and meticulously covered so as to protect from sunlight
3 hours later, the patient returns for a the light treatment with takes 10 to 15 minutes
During treatment minor pain is always experienced which is an indication that the desired reaction is occurring.
A small percentage of patients experience more intense pain and may require local anaesthesia
A light dressing is applied to the area after treatment
The treated area usually has a mild burning or stinging sensation for the first 24 hours, analgesia is rarely required for this.
As with the treatment, a small percentage of patients do experience more intense pain and require analgesia
The treated area becomes red as if sunburned, and will usually peel over the course of a week.
Occasionally blistering and/or scabbing may occur. This indicates a stronger reaction and is normal.
It is essential to stay out of the sun for the remainder of the day of treatment as the area will be particularly sensitive to sun light.
For skin cancers, generally 2 treatments spaced 2 to 4 weeks apart are necessary. For most of the remainder of the conditions a single treatment is adequate.
- Some antibiotics such as tetracyclines (doxycycline)
- Antihypertensives eg thiazides
- Antifungals eg griseofulvin
- Antidiabetic eg sulphonylureas
- Antipsychotics eg phenothiazine
What are the advantages of PDT?
- Safe, with no serious die effects or complications
- Cost effective
- Excellent clinical results
- Excellent cosmetic results
- Able to be repeated
- Suitable for all skin types
What are the disadvantages of PDT?
- Painful for a small percentage of patients
- Limited by the depth of penetration of both the cream and the light, so that only superficial skin can be treated
- Limited by inability to assure complete eradication of skin cancer as there is not confirmatory pathology as part of the treatment
It is critical, therefore, that PDT only be used for the appropriate skin cancer types.
